IMO 기하 문제 풀이 (2020년 ~ 2024년)
추천글 : 【기하학】 IMO 기하 문제 풀이 종합
IMO 2020, Problem 1. Consider the convex quadrilateral ABCD. The point P is in the interior of ABCD. The following ratio equalities hold:
∠PAD : ∠PBA : ∠DPA = 1 : 2 : 3 = ∠CBP : ∠BAP : ∠BPC.
Prove that the following three lines meet in a point: the internal bisectors of angles ∠ADP and ∠PCB and the perpendicular bisector of segment AB.
○ 풀이. Evan Chen의 풀이
○ 풀이. AlphaGeometry를 사용할 때, 새로운 점을 추가하는 AlphaGeometry 모드로 풀립니다. (∵ 더 어려운 문제) (ref)
IMO 2021, Problem 3. Let D be an interior point of the acute triangle ABC with AB > AC so that ∠DAB = ∠CAD. The point E on the segment AC satisfies ∠ADE = ∠BCD, the point F on the segment AB satisfies ∠FDA = ∠DBC, and the point X on the line AC satisfies CX = BX. Let O1 and O2 be the circumcenters of the triangles ADC and EXD, respectively. Prove that the lines BC, EF, and O1O2 are concurrent.
○ 풀이. Evan Chen의 풀이
○ 풀이. AlphaGeometry로 풀리지 않았습니다. (ref)
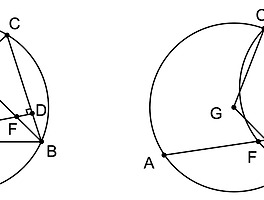
IMO 2021, Problem 4. Let Γ be a circle with center I, and ABCD a convex quadrilateral such that each of the segments AB, BC, CD and DA is tangent to Γ. Let Ω be the circumcircle of the triangle AIC. The extension of BA beyond A meets Ω at X, and the extension of BC beyond C meets Ω at Z. The extensions of AD and CD beyond D meet Ω at Y and T, respectively. Prove that
AD + DT + TX + XA = CD + DY + YZ + ZC.
○ 풀이. Evan Chen의 풀이
○ 풀이. AlphaGeometry를 사용할 때, 새로운 점을 추가하는 AlphaGeometry 모드로 풀립니다. (∵ 더 어려운 문제) (ref)
IMO 2022, Problem 4. Let ABCDE be a convex pentagon such that BC = DE. Assume that there is a point T inside ABCDE with TB = TD, TC = TE and ∠ABT = ∠TEA. Let line AB intersect lines CD and CT at points P and Q, respectively. Assume that the points P, B, A, Q occur on their line in that order. Let line AE intersect CD and DT at points R and S, respectively. Assume that the points R, E, A, S occur on their line in that order. Prove that the points P, S, Q, R lie on a circle.
○ 풀이. Evan Chen의 풀이
○ 풀이. AlphaGeometry를 사용할 때, 새로운 점을 추가하지 않는 DD+AR 모드로 풀립니다. (ref)
==========================
* From theorem premises:
B C D E T A P Q R S : Points
ED = BC [00]
TC = TE [01]
TB = TD [02]
∠TBA = ∠AET [03]
P,A,B are collinear [04]
D,P,C are collinear [05]
Q,A,B are collinear [06]
Q,T,C are collinear [07]
E,A,R are collinear [08]
D,R,C are collinear [09]
E,A,S are collinear [10]
D,T,S are collinear [11]
* Auxiliary Constructions:
: Points
* Proof steps:
001. ED = BC [00] & TC = TE [01] & TB = TD [02] (SSS)⇒ ∠EDT = ∠CBT [12]
002. ED = BC [00] & TC = TE [01] & TB = TD [02] (SSS)⇒ ∠DET = ∠BCT [13]
003. ED = BC [00] & TC = TE [01] & TB = TD [02] (SSS)⇒ ∠DTE = ∠BTC [14]
004. ∠EDT = ∠CBT [12] & D,T,S are collinear [11] ⇒ ∠EDS = ∠CBT [15]
005. ∠DET = ∠BCT [13] & Q,T,C are collinear [07] ⇒ ∠DET = ∠BCQ [16]
006. E,A,S are collinear [10] & Q,A,B are collinear [06] & ∠AET = ∠TBA [03] ⇒ ∠SET = ∠TBQ [17]
007. D,T,S are collinear [11] & Q,T,C are collinear [07] & ∠DTE = ∠BTC [14] ⇒ ∠STE = ∠BTQ [18]
008. ∠SET = ∠TBQ [17] & ∠STE = ∠BTQ [18] (Similar Triangles)⇒ TS:TQ = TE:TB [19]
009. TS:TQ = TE:TB [19] & TB = TD [02] & TC = ET [01] ⇒ TS:TQ = TC:TD [20]
010. D,T,S are collinear [11] & Q,T,C are collinear [07] ⇒ ∠STQ = ∠DTC [21]
011. TS:TQ = TC:TD [20] & ∠STQ = ∠DTC [21] (Similar Triangles)⇒ ∠TSQ = ∠DCT [22]
012. ∠TSQ = ∠DCT [22] & D,T,S are collinear [11] & Q,T,C are collinear [07] ⇒ ∠DSQ = ∠DCQ [23]
013. ∠TBA = ∠AET [03] & ∠EDS = ∠CBT [15] & ∠DET = ∠BCQ [16] & ∠DSQ = ∠DCQ [23] (Angle chase)⇒ ∠(AE-CD) = ∠(QS-AB) [24]
014. Q,A,B are collinear [06] & P,A,B are collinear [04] & E,A,S are collinear [10] & E,A,R are collinear [08] & D,R,C are collinear [09] & D,P,C are collinear [05] & ∠(QS-AB) = ∠(AE-CD) [24] ⇒ ∠SQP = ∠SRP [25]
015. ∠SQP = ∠SRP [25] ⇒ Q,S,P,R are concyclic
==========================
입력: 2024.05.05 21:54
'▶ 자연과학 > ▷ 기하학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 【AlphaGeometry】 jgex_ag_231 기하 문제 풀이 [01-20] (0) | 2024.08.07 |
|---|---|
| 【AlphaGeometry】 jgex_ag_231 문제 재구성 및 풀이 (2) | 2024.08.01 |
| 【국제수학올림피아드】 IMO 기하 문제 풀이 (2015년 ~ 2019년) (0) | 2024.05.05 |
| 【국제수학올림피아드】 IMO 기하 문제 풀이 (2010년 ~ 2014년) (2) | 2024.05.05 |
| 【국제수학올림피아드】 IMO 기하 문제 풀이 (2005년 ~ 2009년) (0) | 2024.05.05 |


최근댓글