RNA 시퀀싱 quality control (QC)
추천글 : 【생물정보학】 생물정보학 분석 목차
1. 실험 QC [본문]
2. 데이터 QC [본문]
3. 트러블슈팅 [본문]
b. 전사체 분석 파이프라인
1. 실험 QC(sample level quality control) [목차]
⑴ 정의 : 조직의 품질을 평가하는 척도
⑵ RNA 시퀀싱 과정
① step 1. RNA 정제 : DNA를 제거하기 위해 DNAse 처리
② step 2. poly A selection
③ step 3. RNA를 library inert size인 200-400 nt로 절편화
④ step 4. RNA를 cDNA로 전환
⑤ step 5. cDNA 가공 : ligate adaptor, amplify, barcode
⑥ step 6. 절편의 한쪽 또는 양쪽을 시퀀싱 : 보통 리드 당 50, 100, 150 nt
⑦ step 7. 시퀀싱 리드를 게놈에 맵핑
⑶ 종류 1. RIN (RNA integrity number)
① 배경지식 : mRNA는 전체 RNA 중 3% 이하. rRNA는 80% 이상 (진핵세포의 경우 주로 28S (2 kb), 18S (5 kb))
② Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer에 의해 측정됨
③ RIN 알고리즘 : 전체 RNA 대비 18S의 비율, 전체 RNA 대비 28S의 비율, 18S normalized height 등의 피처를 이용
④ RIN = 10 : 온전한 RNA
⑤ RIN = 1 : 완전히 degradation이 된 RNA
⑥ RIN > 7 : 일반적으로 RNA-seq을 하기 적합한 퀄리티 수준
⑷ 종류 2. DV200 : FFPE 조직의 경우 RNA가 끊어져 있어서, 200 nt 정도 되는 조각이 몇 %인지를 보는 것
⑸ 종류 3. 흡광도 비를 통한 핵산 순도 정량
① 260 nm / 280 nm ratio
○ 순수한 DNA : ~1.8
○ 순수한 RNA : ~2.0
○ 낮은 260 nm / 280 nm 비는 280 nm에서 흡광도를 보이는 단백질, 페놀이 포함돼 있음을 의미함
② 260 nm / 230 nm ratio
○ 순수한 DNA / RNA 분자 : ~2-2.2
○ 낮은 260 nm / 230 nm 비는 다른 contaminant의 존재를 암시함
⑹ 종류 4. 핵산 무게 정량
① miRNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN) 등을 통해 RNA를 추출
② RNA 무게 기준 : 250 ng 이상
⑺ 종류 5. RNA quality score (RQS)
⑻ 종류 6. ChIP-seq 실험 QC
① ChIP grade 단일 클론 항체 : ChIP-seq을 미리 테스트한 항체. 시판 항체의 20-35%는 ChIP-seq에 적합하지 않음
② IgG (non-specific antibody) : IgG에 비해 관심 항체의 qPCR 결과가 10-12배 이상이 돼야 함
③ 전사인자에 비오틴을 붙임 : streptavidin 하에 침전됨. 항체에 무관한 실험 QC 기법
④ CUT&RUN, CUT&Tag, ChIP-exo가 ChIP-seq을 개선하는 데 사용될 수 있음
⑼ 종류 7. ATAC-seq 실험 QC
① Tn5 농도 : DNA 농도 대비 Tn5 농도가 높을수록 프로모터 및 인핸서에서 ATAC-seq 신호 강도가 증가하고 fragment 사이즈가 감소
② 시퀀싱 lane cluster density : fragment length distribution과 TSS enrichment에 shift를 일으킴
⑽ 종류 8. 공간전사체 실험 QC (ref)
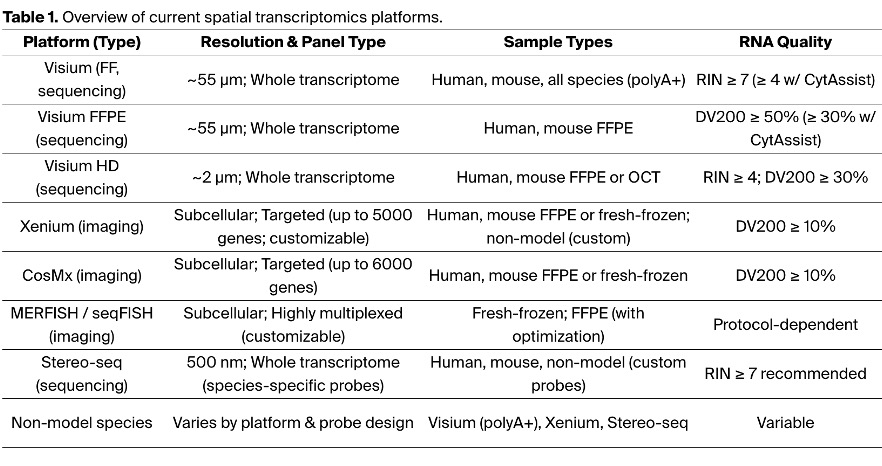
Table. 1. 공간전사체 실험 QC
① fresh-frozen tissue가 FFPE보다 RNA integrity가 더 높고 tissue morphology 퀄리티가 나쁨
② FFPE의 경우 DV200이 더 적절한 메트릭
③ Xenium이나 CosMx 같은 image 기반 ST는 spot 기반 ST보다 RNA degration을 더 잘 tolerate할 수 있음
2. 데이터 QC(sequence level quality control) [목차]
⑴ 정의 : 데이터의 품질을 평가하고, 필요시 개선하는 것
⑵ 종류 1. 데이터 QC 메트릭 : 메뉴얼 혹은 다른 데이터셋과 비교하여 external validity 확인 목적
① QC 메트릭
○ dUTP method 기준, "_1.fastq"는 first strand (anti-sense)이고, "_2.fastq"는 second strand (sense; 원래 RNA 서열)
○ base quality
○ mapping rate
○ mappability filter
○ 종류 1. uniqueness : 특정 염기에서 시작하고 특정 길이를 가지는 서열이 얼마나 고유한지
○ 종류 2. alignability : k-mer 서열이 게놈의 특정 영역에 얼마나 고유하게 정렬되는지 (최대 2개의 불일치 허용)
○ mappability score : S = 1 / # of matches found in genome
○ long read에서는 mapping rate가 증가함 : 단, 반복서열은 long read여도 개선되지 않을 수 있음
○ non-coding RNA 비율
○ non-coding RNA 비율이 높으면 RNA 퀄리티가 낮음을 의미
○ GC 함량(GC content)
○ GC 함량이 너무 높은 경우 : rRNA contamination이 있을 가능성이 높음. 이 경우 5S, 18S, 28S rRNA를 필터링해야 함
○ GC 함량이 너무 낮은 경우 : 역전사 반응이 제대로 되지 않을 가능성이 높음
○ CpG island와 관련 있음
○ read duplicate
○ PCR duplicate : 같은 핵산 분자가 PCR 하에서 복제된 것에 불과한 것. duplication이 많으면 RNA 퀄리티가 낮음을 의미
○ 완전히 같은 서열을 가지면 PCR duplicate, 유사하면 biological duplicate으로 보기로 간주
○ paired-end 실험의 경우 paired-end 수준에서 duplicate가 발생함
○ 일반적으로 DNA-seq은 duplicates를 제거하고, RNA-seq은 제거하지 않음 : RNA-seq에서는 기술적 중복뿐만 아니라, 높은 발현량을 가지는 전사체(high expressing transcripts)나 짧은 유전자(short genes)로 인해 동일한 서열이 반복적으로 관찰될 수 있음. 이러한 생물학적 중복을 제거하면 데이터의 동적 범위(dynamic range)가 줄어들거나 통계적 검출 능력(powers)이 감소할 위험이 있음
○ PCR 과정에서 사이클 수가 증가하면 중복률이 높아질 가능성이 있음 : 중복률이 PCR 사이클 수와 높은 상관관계를 가지는지 확인함으로써, 기술적 중복인지 생물학적 중복인지 구분할 수 있음
○ duplicate를 제거하는 툴 : Samtools, Picard, Trimmomatic, Trim Galore!, fastp
○ unique molecule(UMI)
○ unique molecule이 10% 미만인 경우 RNA 퀄리티가 상당히 낮음을 의미
○ sequencing depth
○ 리드의 수
○ alternative splicing 혹은 allele-specific 발현의 경우 : > 50 million 리드가 권장됨
○ ribo-depleted library의 DEG 분석 : 전체 ~50-60 million 리드가 권장됨
○ ribo-depleted library는 poly-A selected library보다 두 배 더 많은 sequencing depth가 권장됨 : ribo-depleted library는 poly-A selected library는 포착할 수 없는 더 다양한 RNA(예 : tRNA, rRNA, 미성숙 RNA)를 포착할 수 있기 때문
○ sequencing read length
○ sequencing fragment가 너무 작으면 adaptor가 읽히기 시작함 : 이 경우 adaptor cut을 함

Figure. 1. fragment가 짧으면 adaptor가 읽히는 이유
○ short-read seq 대비 long-read seq의 장점 : nt 당 비용은 더 낮음. 더 정확한 맵핑. splice junction 위치를 알 수 있음. allele 특이적 발현을 알 수 있음. 반복서열을 알 수 있음
○ short-read seq 대비 long-read seq의 단점 : 전체 비용은 더 높음. read 당 비용은 더 높음. 더 많은 adaptor trimming을 요함 (∵ long-read (PacBio, Oxford Nanopore)는 시퀀싱 방식 자체(반복적인 읽기, single-molecule sequencing) 때문에 adapter가 더 많이 포함될 가능성이 큼)
○ adaptor sequence
○ 문제점 1. adaptor sequence는 인위적인 서열이므로 alignment, variant calling이 실패하거나 bias가 생기게 함
○ 문제점 2. adaptor sequence는 동일한 서열들을 포함하기 때문에 coverage analysis, DEG 분석 등에 bias가 생기게 함
○ adaptor sequence를 제거하기 위해 AdaptorRemoval, Cutadapt, Trimmomatic, bbduk.sh 등이 사용됨
○ exonic 비율
○ poly-A(+) RNA-seq의 경우 exonic이 50 ~ 70%
○ rRNA(-) RNA-seq의 경우 exonic의 비율이 적어짐
○ paired-end vs single-end
○ single-end : 한쪽 끝에서 시퀀싱됨
○ paired-end : 양쪽 끝에서 시퀀싱됨
○ paired-end (PE) reads는 single-end (SE) reads에 비해 더 정확한 반면 가격이 2배 정도로 비쌈
○ 단순히 목적이 유전자 카운트를 구해서 DEG 분석을 하는 것이라면 SE도 충분함
○ RNA가 상당히 degradation 돼 있으면 SE가 권장됨
○ 짧은 fragment에 PE를 써서 같은 뉴클레오티드가 시퀀싱되는 비효율은 피하는 게 좋음

Figure. 2. PE에서 생길 수 있는 비효율
○ mate pair read
○ DNA 세그먼트가 circularize 된 경우 결합한 지점에서 양쪽으로 시퀀싱을 하여야 함
○ strand-specific (ssRNA-seq)
○ forward 혹은 reverse 중 하나
○ poly-A selection vs ribo-depletion
○ ribo-depletion library의 장점
○ RNA degradation에도 가능 : cDNA 길이가 일정하지 않고 짧음. poly-A selection은 매우 3'에 편향돼 부정확함
○ non-coding RNA를 연구할 때 적합함
○ ribo-depletion library의 단점
○ 비쌈
○ 의미 없는 리드들이 많이 포함돼 있음
② ChIP-seq QC 메트릭
○ read depth : ENCODE 권장 기준은 uniquely mapped reads가 10 million 이상
○ background uniformity (biasedness)
○ qPCR enrichment
○ input DNA qualuty via NanoDrop
○ cross-correlation analysis : NSC (normalized strand coefficient), RSC (relative strand correlation)
○ FRiP (fraction of reads in peaks), RUP(reads under peaks) : 피크로 잡힌 신호의 비율. ENCODE 권장 기준은 1% 이상
○ SPOT(signal portion in tags) : 피크로 잡힌 신호의 비율
○ IDR (irreproducibility discovery rate) (ref1, ref2)
○ denQCi, simQCi, QC-STAMP (ref)
○ motif analysis : 피크의 몇 %가 TF motif를 포함하는지, motif가 피크의 중간에 나타나는지 (heterodimer 등은 아닐 수 있음)
③ ATAC-seq QC 메트릭
○ FastQC : 예를 들어, per base sequence content를 통해 Tn5 transposase의 integration bias를 평가할 수 있음
○ ataqv 패키지는 다음과 같이 35가지 QC 메트릭을 제공함 (ref) : fragment length distribution, % reads that are high-quality and autosomal, % reads properly paired end mapped, % reads that aligned to autosomes that were duplicates, short-to-mononucleosomal-ratio, TSS enrichment, duplicate fraction in peaks, duplicate fraction outside of peaks, peak duplicate ratio, cumulative fraction of high-quality autosomal reads in peaks, cumulative fraction of the genome that falls within peaks, distribution of mapping qualities, number of total reads, % alignments marked secondary, % alignments marked supplementary, % alignments marked as duplicates, mean mapping quality, median mapping quality, % reads unmapped, % reads with an unmapped mate, % QC-fail reads,% unpaired reads, % reads with mapping quality 0, % reads that paired and mapped but in RF orientation, % reads that paired and mapped but in FF orientation, % reads that paired and mapped but in RR orientation, % reads that paired and mapped but on separate chromosomes, % reads that paired and mapped but too far from mate, % reads that paired and mapped but not properly, % reads that aligned to autosomes, % reads that aligned to mitochondria, % reads that aligned to mitochondria that were duplicate, number of peaks called, fragment length distribution distance, max fraction of reads from a single autosome
④ 방법 1. 다른 데이터셋 : 10x Genomics, GEO, ZENODO 등
⑤ 방법 2. FastQC : Fastq 파일을 입력으로 함
○ 2-1. FastQC와 multiQC : 가장 많이 사용
○ base pair quality of reads
○ adaptor sequences in reads
○ PCR duplicates
○ overrepresented sequences
○ 샘플별 GC distribution
○ 2-2. QoRTs (ref1, ref2) : 매우 좋음
○ RNA degradation : 5' → 3'으로 read가 분포
○ strandedness check
○ GC bias
○ 2-3. RNASeQC : 준수함
○ 2-4. RSeQC : 몇몇 주요한 버그가 있어서 문제가 됨
○ 2-5. conda Fastqc 명령어 사용 (리눅스)
○ 2-6. SRA (Sequence Reads Archive) Toolkit을 다운받은 후 fastqc 명령어 사용
○ 실제 생성 파일 예시 : DRR016938_fastqc.html
sudo apt install fastqc
cd sratoolkit.3.0.5-ubuntu64/
cd bin
fastqc DRR016938.fastq
⑥ 방법 3. Trimmomatic : Fastq 파일을 입력으로 함
⑦ 방법 4. FASTX-Toolkit : Fastq 파일을 입력으로 함
⑧ 방법 5. 맵핑 이후의 QC : SAM 혹은 BAM 파일을 입력으로 함
○ QC 메트릭
○ % uniquely mapped reads
○ % reads mapping to exons
○ 복잡성, 즉 x% of read counts being taken up by y% of genes
○ 샘플에 따른 일관성
○ 샘플이 바꼈는지 여부(sample swap) : Y 염색체, Xist, SNP 등의 정보를 메타데이터와 매칭
○ 5-1. Qplot
○ 5-2. Samtools
⑨ 방법 6. SnakeMake : 통합 파이프라인이므로 QC 기능도 제공됨
○ Snakefile : 파일명이 Snakefile. SnakeMake 스크립트로서 파이썬을 기반으로 함
# Snakefile
# 결과 파일을 정의
rule all:
input:
"results/processed_data.tsv"
# 데이터 처리 규칙
rule process_data:
input:
"data/raw_data.tsv"
output:
"results/processed_data.tsv"
shell:
"""
cat {input} | awk -F'\t' '{{print $1, $2, $3}}' > {output}
"""
○ config.yaml (선택적) : Snakemake workflow의 설정
○ requirements.txt (선택적) : 패키지 dependency
○ 입력 파일
○ 출력 파일
⑩ 방법 7. QuASAR-QC : Hi-C seq 데이터에 적용
⑪ 트러블슈팅
⑶ 종류 2. 샘플 간의 rank-correlation : internal validity 확인 목적
① 목적 1. 하나의 샘플 내에 정렬 특성이 있는 두 변량의 alignment를 살펴서 샘플의 품질을 평가할 수 있음
○ 예 1. 서로 유사하다고 알려진 두 유전자의 발현 정도의 alignment를 살피는 것
○ 예 2. 서로 유사하다고 알려진 두 유전자 발현이 비슷한 클러스터에서 나타나는지 살피는 것
② 목적 2. 동일한 한 쌍의 샘플의 correspondence를 보는 때 주로 사용함
③ 목적 3. 데이터 분포 특성이 다른 서로 다른 두 변량의 상관계수를 조사할 수 있음
○ QC 분석과는 다소 거리가 있는 개념
○ 예시 : scRNA-seq에서의 어떤 유전자 A 발현과 ST에서의 A 발현의 상관계수를 조사하는 경우
④ 방법 1. Pearson 상관계수
○ 정의 : X와 Y의 표준편차 σx, σy에 대해,
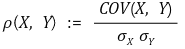
○ 특징
○ 등간, 비율척도로 측정된 두 변수들의 상관관계
○ 연속형 변수를 대상으로 함
○ 정규성 가정
○ 대부분 많이 사용
○ cor(x, y)
○ cor(x, y, method = "pearson")
○ cor.test(x, y)
○ cor.test(x, y, method = "pearson")
⑤ 방법 2. Spearman 상관계수
○ 정의 : x' = rank(x)와 y' = rank(x)에 대해 다음과 같이 정의
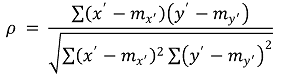
○ 특징
○ 서열 척도인 두 변수들의 상관관계를 측정하는 방식
○ 순서형 변수를 대상으로 하는 비모수적 방법
○ 제로가 많은 데이터에 유리함
○ 데이터 내 편차나 에러에 민감
○ 켄달 상관계수보다 높은 값을 가짐
○ cor(x, y, method = "spearman")
○ cor.test(x, y, method = "spearman")
⑥ 방법 3. Kendall 상관계수
○ 정의 : concordant pair와 discordant pair에 대해 상관계수를 정의
○ 특징
○ 서열 척도인 두 변수들의 상관관계를 측정하는 방식
○ 순서형 변수를 대상으로 하는 비모수적 방법
○ 제로가 많은 데이터에 유리함
○ 샘플 사이즈가 작거나 데이터의 동률이 많을 때 유용함
○ 절차
○ step 1. x 값에 대한 오름차순으로 y 값을 정렬 : 각 y 값을 yi로 표기
○ step 2. 각 yi 값에 대하여 yj > yi (단, j > i)인 concordant pair의 개수를 셈
○ step 3. 각 yi 값에 대하여 yj < yi (단, j > i)인 discordant pair의 개수를 셈
○ step 4. 상관계수 정의
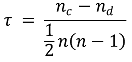
○ nc : total number of concordant pairs
○ nd : total number of discordant pairs
○ n : size of x and y
○ cor(x, y, method = "kendall")
○ cor.test(x, y, method = "kendall")
⑦ 방법 4. empirical CDF(누적분포함수) 간의 Q-Q plot
⑧ 방법 5. ordered p-value 간의 Q-Q plot
⑨ (참고) Hi-C seq의 경우, HiCRep, GenomeDISCO, HiC-Spector, QuASAR-Rep가 있음
3. 트러블슈팅 [목차]
⑴ 방법 1. 웹사이트 조사 : pre-fligh error, in-flight error 또는 alerts
① Failing to install bcl2fastq
② ATAC Sequencing depth per cell is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 10,000. Low ATAC sequencing depth negatively impacts the quality of peak calling, clustering, differential analysis and feature linkage. At very low sequencing depth, < 5000 raw read-pairs per cell, identification of cell barcodes may be unreliable.
③ GEX Sequencing depth per cell is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 5,000. Low GEX sequencing depth negatively impacts the quality of clustering, differential analysis and feature linkage. At very low sequencing depth, < 2,000 raw read-pairs per cell, identification of cell barcodes may be unreliable.
④ ATAC Median fragments per cell is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : A low value is generally caused by low sequence depth, the wrong genome reference, or low library complexity that could be due to a problem during the transposition step or a problem in the library preparation workflow. Low fragment counts negatively impact clustering, differential analysis and feature linkage detection.
⑤ Number of linkages detected is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : The number of detected feature linkage is < 100. This may be caused by a low number of nuclei recovered, low sequencing depth, poor peak calling, or a sample that is relatively homogenous.
⑥ GEX Median UMI counts per cell is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Observed value < 100. This may be a consequence of very low sequencing depth, poor sample quality, an error in the library preparation workflow, the wrong reference genome, or poor genome annotations. Low UMI counts negatively impact clustering, differential analysis and feature linkage detection.
⑦ GEX Reads mapping to reference is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 80%. This can be caused by the wrong reference genome being used or a poor quality genome assembly. Application performance may be affected.
⑧ GEX Reads mapping to transcriptome is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 50%. This can indicate use of the wrong reference transcriptome, a reference transcriptome with overlapping genes, poor library quality, poor sequencing quality, or reads shorter than the recommended minimum. Application performance may be affected.
⑨ ATAC Reads mapping to reference is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 80%. This can be caused by the wrong reference genome being used or a poor quality genome assembly. Application performance may be affected.
⑩ GEX Transcriptome reads in cells is low (Cell Ranger ARC v2.0) : Ideal > 60%. Many of the reads were not assigned to cell-associated barcodes. This is generally indicative of poor sample prep resulting in high levels of ambient RNA. It could also indicate a problem in the cell calling algorithm that could be caused by high RNA or DNA background, exclusion of a large number of barcodes from cell calling due to low targeting, or due to a population of nuclei with low RNA content. The latter case can be addressed by inspecting the data to determine the appropriate cell count and rerunning the pipeline supplying appropriate parameters to override the cell caller. Application performance may be affected.
⑪ Low Fraction Reads Confidently Mapped To Transcriptome (Cell Ranger v6.1) : Ideal > 30%. This can indicate use of the wrong reference transcriptome, a reference transcriptome with overlapping genes, poor library quality, poor sequencing quality, or reads shorter than the recommended minimum. Application performance may be affected.
⑫ No Cells Detected (Cell Ranger v6.1) : Estimated number of cells is expected to be > 100. This usually indicates poor cell handling, poor library, or poor sequencing quality. Application performance is likely to be affected.
⑬ Low Fraction Valid UMIs (Cell Ranger v6.1) : Ideal > 75%. This may indicate a quality issue with the Illumina R2 read for Single Cell 3' v1 or the R1 read for Single Cell 3' v2/v3 and Single Cell 5'. Application performance may be affected.
⑭ Fraction of UMI bases with Q-score >= 30 is low (Cell Ranger v6.1) : Fraction of UMI bases (Illumina R2 Read for Single Cell 3' v1, R1 for Single Cell 3' v2/v3 and Single Cell 5') with Q-score >= 30 should be above 75%. A lower fraction might indicate poor sequencing quality.
⑮ Fraction of cell barcode bases with Q-score >= 30 is low (Cell Ranger v6.1) : Fraction of cell barcode bases (Illumina I7 Read for Single Cell 3' v1, R1 for Single Cell 3' v2/v3 and Single Cell 5') with Q-score >= 30 should be above 55%. A lower fraction might indicate poor sequencing quality.
ⓐ Too many detected cells (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : Estimated number of cells is expected to be under 10,000. A high value might indicate an overlapping of cells, a problem during library preparation, or unexpected behavior in the cell calling algorithm.
ⓑ Average fraction of barcode bases with high sequencing quality is low (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : Average fraction of bases in barcode with quality above Q30 should be ideally above 75%. A lower fraction might indicate poor sequencing quality.
ⓒ Median fragments per cell is low (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : The median number of fragments (that passed all filters) detected in single cells is expected to be above 500. A lower value suggests low sensitivity, potentially due to insufficient sequencing.
ⓓ The percentage of transposition events falling within peaks is low (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : It is expected that more than 25% of the transposition events fall within peak regions. A lower value could suggest peak undercalling or low sequencing depth.
ⓔ Estimated number of cells is low (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : Number of cells detected is expected to be higher than 500. This usually indicates poor cell, library, or sequencing quality.
ⓕ Average fraction of barcode bases with high sequencing quality is low (Cell Ranger ATAC v2.0) : Average fraction of bases in barcode with quality above Q30 should be above 75%. A lower fraction might indicate poor sequencing quality.
ⓖ Fraction of RNA read bases with Q-score >= 30 is low (Space Ranger v1.3) : Fraction of RNA read bases with Q-score >= 30 should be above 80%. A lower fraction might indicate poor sequencing quality.
ⓗ Low Fraction Reads in Spots (Space Ranger v1.3) : Ideal > 50%. Application performance may be affected. Many of the reads were not assigned to tissue covered spots. This could be caused by high levels of ambient RNA resulting from inefficient permeabilization or because of poor tissue detection. The latter case can be addressed by using the manual tissue selection option through Loupe.
⑵ 방법 2. technical note 조사
① Single Cell Gene Expression Assay
② Single Cell Multiome ATAC + Gene Expression Assay
입력: 2023.05.22 11:48
'▶ 자연과학 > ▷ 생물정보학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 【생물정보학】 생물정보학 데이터 형식 이해하기 (0) | 2023.08.03 |
|---|---|
| 【생물정보학】 셀 타입 마커 유전자 (2) | 2023.07.05 |
| 【생물정보학】 모델 생물 라이브러리 (0) | 2022.07.20 |
| 【생물정보학】 bulk RNA-seq에서 DEG 획득하기 (DESeq2, t test, ANOVA) (0) | 2022.07.02 |
| 【생물정보학】 유전자 스코어 라이브러리 (0) | 2022.06.21 |


최근댓글